The DIFOWT Project
De-risking Ireland’s Floating Offshore Wind Targets
What is DIFOWT
The DIFOWT (De-Risking Ireland’s Floating Offshore Wind Targets) Project aims to address the challenges facing investment for Ireland’s ports, vessels and workforce requirements, while also helping to influence and expand the scope of policy frameworks for the growth of Ireland’s Floating Offshore Wind (FOW) sector. Some of the key infrastructural areas to target for investment include port and wet storage capacity, vessels, farm availability and LCOE sensitivity.
This investment challenge is a clear ‘bottleneck’ which had been identified by a previous SEAI RD&D funded project, SIMREI (Support Infrastructure for Marine Renewables in Ireland), which developed models of the installation, operation and maintenance of Floating offshore Wind Farms in Irish water. These models were then used to determine the required scale of port infrastructure and vessels to deliver Ireland’s goals for offshore wind capacity.
Offshore wind energy is expected to provide substantial renewable energy capacity for Ireland, including reaching 5 GW of ORE (offshore renewable energy) to be provided by 2030 and at least 37 GW by 2050.
-
Project duration is January 2024 – December 2025.
- Contact us: research@windenergyireland.com
Project Objectives
The DIFOWT project aims to de-risk Ireland’s FOW sector to ensure its timely and economically viable development. To achieve this, the project will engage with stakeholders to identify and confirm current industry risks, use simulations to provide quantitative evidence of these risks’ impacts, and simulate the future development of FOW in Ireland up to 2050 to understand the broader implications for national targets.
Additionally, the project will disseminate evidence-based recommendations and outputs to stakeholders to mitigate risks and accelerate the development and commercialization of FOW in Ireland.
Project Outputs
The outputs of DIFOWT will de-risk Ireland’s FOW sector and be used to guide policy and leverage investment for port and infrastructure development as well as the procurement of appropriate vessels and better understanding of key requirements.
The outputs will include the results and analysis of simulations designed to model the FOW development pipeline in Ireland. The simulations will put to test general assumptions associated with FOW development and the impact of varying these assumptions. Understanding the risk and quantifying the impact is a key output of the DIFOWT project.
The project will publish regular project updates, which will provide data from the modelling activities for the future use of FOW wind turbines in Irish waters, as well as news from monthly reports from the project partners.
Introduction to DIFOWT project
Listen to Ben Kennedy of Wave Venture, introduce the DIFOWT project.
Floating Wind Risk Management series
.png?width=1280&height=720&name=Floating%20Wind%20Risk%20Management%20Series%20-%20Chapter%201.pdf%20(1).png)
Chapter 1 - Port distance impact on installation
Port distance has a significant impact on a floating wind project development. This chapter presents results from analysing distance from port and the impact on install ability, utilising evidence-based results produced using TEMPEST™.
Download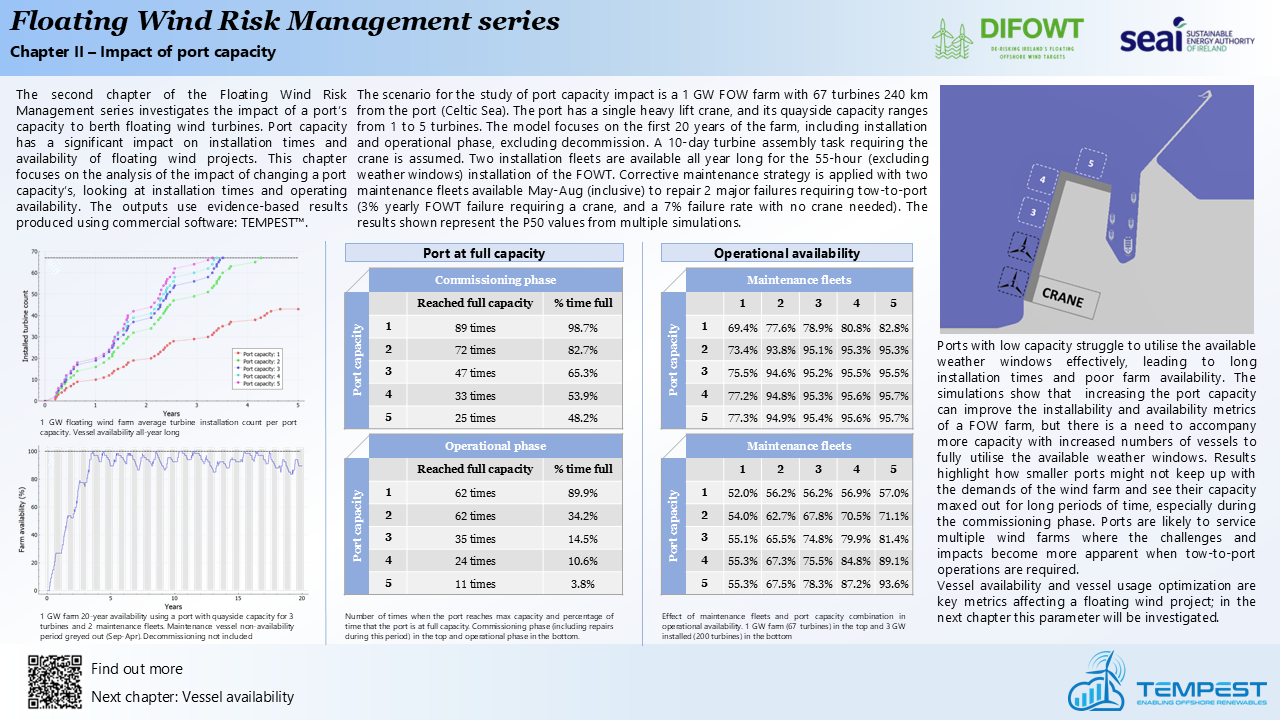
Chapter 2 - Port Capacity
Port capacity has a significant impact on installation times and availability of floating wind projects. This chapter focuses on the analysis of the impact of changing port capacities, looking at installation times and operating availability.
Download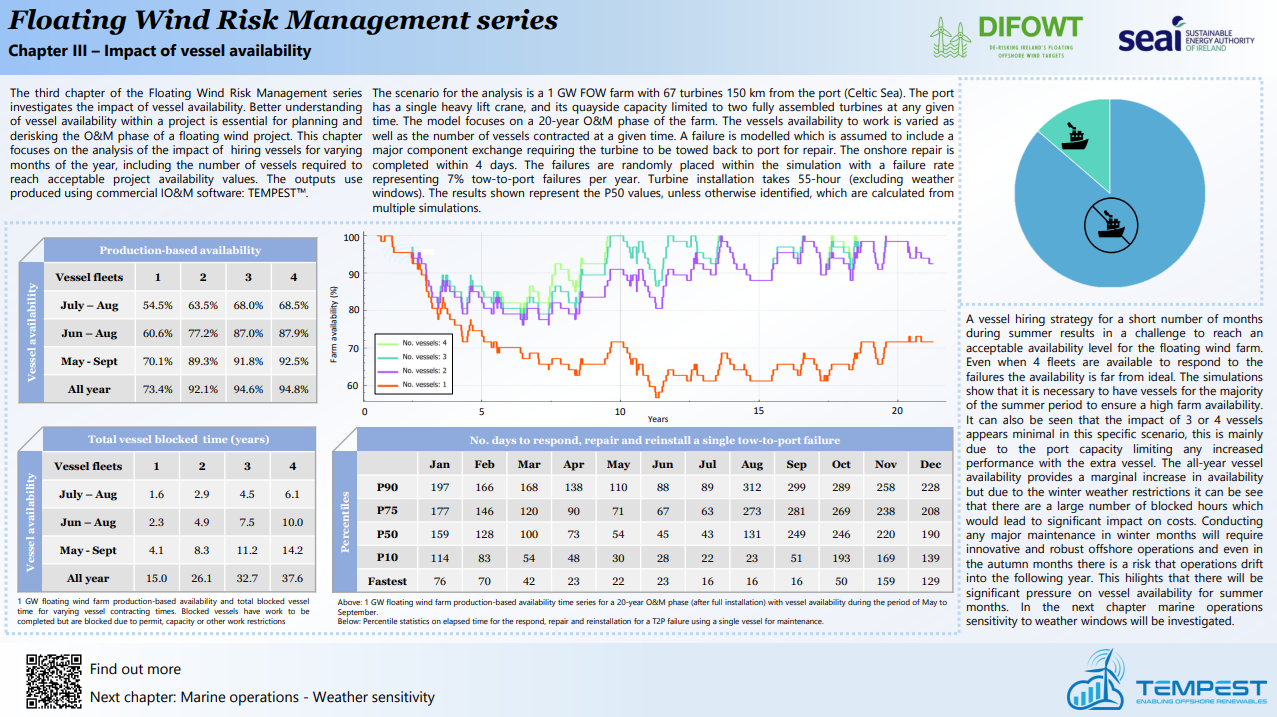
Chapter 3 - Vessel Availability
With floating wind projects, better understanding of vessel availability within a project is essential for planning and derisking the operation and maintenance (O&M) phase. This chapter focuses on the analysis of the impact of hiring vessels for varying months of the year, including the number of vessels required to reach acceptable project availability values.
DownloadSign Up here for DIFOWT Project Updates
Sign up via this form to receive news, progress reports, project outputs and to participate in surveys and interviews on project topics.
Your Contact Details
Our Funding Body
This project has been supported with financial contribution from Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland under the SEAI Research, Development & Demonstration Funding Programme 2023, Grant number 23/RDD/923








